A policy that is being adapted to tackle the resurgence of inflation
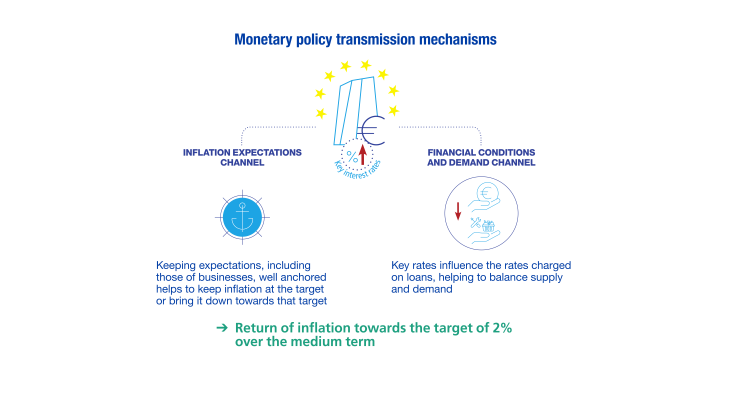
The ECB adapts its monetary policy to meet the target of 2% inflation over the medium term. After more than a decade of deflationary risks, marked by the 2007-08 Global Financial Crisis and then the Covid-19 pandemic, the resurgence of inflation in the euro area between 2022 and 2023 has prompted a sharp change of direction.
Interest rates were raised by an initial 50 basis points (0.5%) on 27 July 2022. Since then, key rates, and hence bank interest rates, have been increased regularly. The aim is to reach a sufficiently restrictive level to lower inflation by curbing demand, and to avoid the risk of inflation expectations becoming too high for too long.
This monetary policy is underpinned by an in-depth assessment of the risks to price stability, based on an integrated analytical framework consisting of two types of analysis.
An economic analysis
ECB experts use a broad range of economic and financial indicators to forecast the future path of prices in the euro area. These include unit labour costs, measures of actual activity, price and cost indicators, surveys of businesses and households, and indicators of financial conditions (effective euro exchange rate, slope of the yield curve, bond yields, etc.). The Governing Council also bases its assessment on the macroeconomic projections published by the ECB each quarter, which are prepared in conjunction with Eurosystem economists, including teams at the Banque de France.
A monetary and financial analysis
This analysis focuses on medium and long-term trends in inflation. It is based on a range of indicators, notably the change in the M3 monetary aggregate, which is the overall supply of money in circulation in the euro area economy. M3 needs to be kept to a growth rate that is compatible with 2% inflation over the medium term.
Incorporation of climate considerations
The 2021 monetary policy strategy review acknowledged that climate change has implications for price stability. As a result, the ECB Governing Council has adopted an action plan aimed at incorporating climate considerations into monetary policy assessments; expanding its analytical capacity in this field; adapting the operational framework for monetary policy; and implementing actions in line with policies on environmental sustainability disclosure and reporting.
Regular reviews of the monetary strategy framework
The Governing Council regularly reviews the effectiveness of its monetary policy strategy. The last review, which was completed in July 2021, was published by the ECB on its website. To tackle inflationary and deflationary risks more effectively, it adopted a price stability target of 2% inflation over the medium term. It also acknowledged that climate change has profound implications for price stability. The next strategy review should take place in 2025.