A 2022 global financial landscape that remains dominated by the United Kingdom and United States
Foreign exchange and financial derivatives markets are concentrated in a few financial centres. Every three years, the Triennial Survey coordinated by the BIS and conducted by the Banque de France for France, provides an overview of the global landscape.
The survey measures notional amounts of over-the-counter (OTC) activity over the month of April.
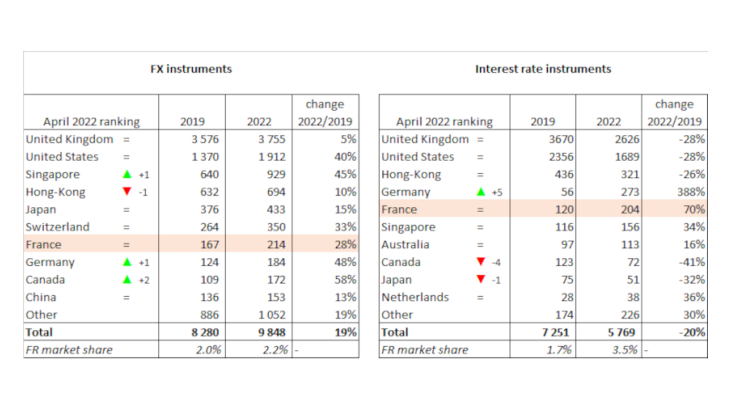
London and the United States continue to top the rankings. Forex activity volumes there are respectively four and two times higher than in the next biggest financial centre (and respectively eight and five times higher for interest rate derivatives). However, activity volumes in London have levelled off in the forex market since 2019 and fallen sharply in interest rate derivatives, whereas rival European centres have seen double-digit growth and have gained market share in both activities.
Whereas Singapore and Hong Kong were jostling for 3rd place in the forex market in 2019, Singapore now ranks well ahead of Hong Kong. The Singapore dollar has expanded its market share from 1.8% to 2.4% of daily global trading volumes, and now stands level with the Hong Kong dollar which in turn has seen a sharp fall in market share. Nevertheless, Singapore continues to lag behind Hong Kong in the interest rate derivatives market.
In the rest of Asia, Japan remains one of the top five centres for forex transactions, but has fallen one place in the rankings for interest rate derivatives. China has remained stable versus 2019 in the forex market at 10th place. Both countries may have been negatively affected by the prolonged maintenance of public health restrictions during the pandemic.
There are also a few standout centres that have seen particularly strong improvements in their rankings: this is notably the case for Germany in interest rate derivatives and Canada in the forex market.
France has maintained its global No. 7 ranking in the FX market
Global forex market activity has risen by 19% in the past three years (gross data adjusted for domestic double counting). This strong growth comes against a backdrop of rising global tensions and the appreciation of the US dollar since the summer of 2021. With a daily volume of USD 214 billion of transactions, compared with USD 167 billion in 2019, the Paris financial centre has expanded in line with global markets, while at the same time maintaining its No. 7 ranking, ahead of Germany.
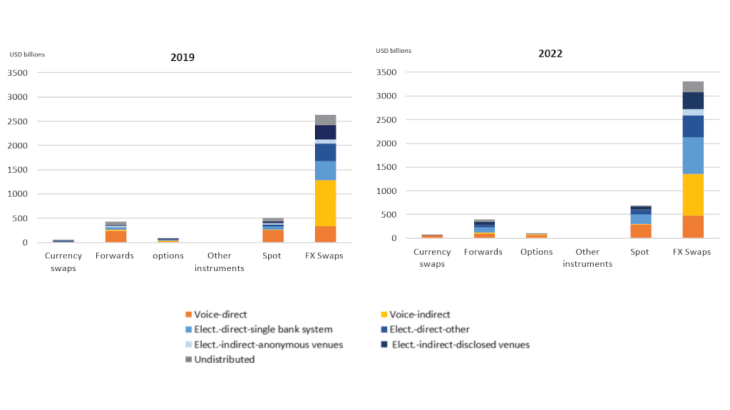
In Paris, activity is highly concentrated among just a few players: four entities account for over 70% of total market activity. They have a strong presence in FX swaps, which is their preferred instrument for managing their cash reserves and hedging their forex risk. France stands out from the rest of the world in this respect: FX swaps are used in 71% of transactions in France compared with an average of 51% globally.
In France and the rest of the world, transaction maturities are becoming shorter: 80% have a maturity of up to one month compared with 77% in 2019 (global average of 84% in 2022). The rise in very short term transactions in part explains the growth in global activity, as contracts are mechanically renewed more often.
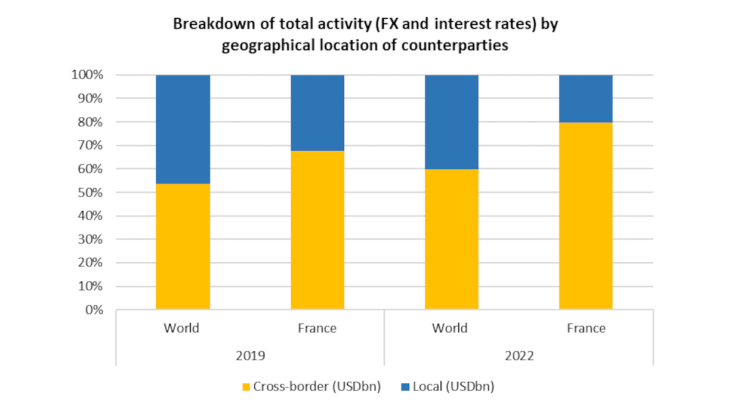
Brexit, which has led several French and foreign institutions to shift large account management activities out of London, has also helped to boost activity volumes in Paris by increasing the number of staff based in France.
In the interest rate market, Paris has maintained its No. 5 global ranking and seen a rise in activity
The notional amount of interest rate derivatives transactions has fallen by 20% globally and by 28% in the United Kingdom and United States between 2019 and 2022 (gross data adjusted for domestic double counting). In contrast, several large European centres have seen sharp growth in activity: rises of 36% in the Netherlands, 70% in France and nearly 400% in Germany. Among the factors that might explain the diverging trends between Anglo-Saxon countries and the main continental European centres are the reforms to interbank benchmark indices, which are at different stages and have differing impacts.
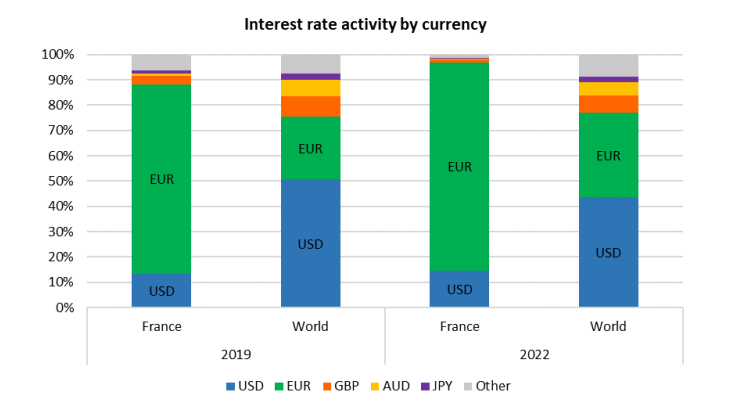
- The end of the use of USD LIBOR in new contracts and the subsequent drop in transactions in the index could explain part of the fall in activity in US and UK markets. The transition from LIBOR to the overnight risk-free rate has also probably changed the need for interest rate risk hedging. In the euro area, Euribor has been reformed but its characteristics and the way it functions have been left unchanged, so there has been less of an impact on activity. In terms of currencies, the share of total interest rate transactions in France that are denominated in euro has risen from 75% to 82% (see Chart 1).
- The move from EONIA to ESTER in 2022 also appears to have prompted changes in strategy and positioning. Several French institutions say they are now focusing their activity more on short-term interest rate instruments and are processing transactions more quickly, leading to a rise in volumes.